Product integration
Product integration combines both delay integration and starting point settings in a single dialog. Using product integration is the first step to complete when optimizing a system. It is not recommended for use when a system has previously been optimized, as some or all of the output processing filters and settings may be over-written.
By selecting the loudspeaker model in the pop-up window, the Delay and Starting Point drop-down menus are populated with the available options.
A video describing product integration in more detail is available at meyersound.com/videos/#support
Delay integration
Delay integration aligns the phase responses of different loudspeaker model families to match predefined target curves.
After selecting the product this setting will apply to, choose the desired target phase curve frequency: 55-70, 100, or 125 (Hz). Different products will have different phase curve options available, though PC125 will be available for every product. Choose the lowest target phase curve that is available for all loudspeaker types in a system.
Some subwoofer delay integration settings also implement filters that change the frequency response of the product. This is necessary to achieve the appropriate phase response to be compatible with the phase curve family.
Starting points
There are two kinds of starting points:
Filter presets for line array models
Delay and polarity settings for the rear-facing element(s) of gradient subwoofer arrays
Line array models
When certain line array products are chosen, the user can select a starting point from the drop-down menu. These presets use U-Shaping filters that adjust the frequency response to a usable result. For most products, the response will be close to equal magnitude (flat) for arrays that are 6-8 elements.
Some line array products have presets that are based on the total splay angle between four elements, shown as Wide, Medium, or Narrow. Choose the setting that best matches the splay angles between the elements this output channel will be driving.
For example, if an output will be driving four elements of a LYON-M array where there is 3° of splay between every element, the total splay between four elements is 9°, and the “Medium” preset would be most appropriate.
Some line array products have a single preset that can be used as a starting point in any configuration. If a line array product does not have a starting point preset available, it is designed to be used in native mode and does not require a preset.
Subwoofers
Starting point settings for some subwoofers provide a choice to select a front or rear-facing subwoofer. These settings are designed for subwoofers being used in gradient configurations that produce cardioid coverage patterns. Selecting a front facing starting point will not implement any processing for most models. Selecting a rear-facing starting point will invert the polarity and implement appropriate delay to synchronize the output of the rear-facing element with the output behind the array of the front-facing elements. This delay is applicable to subwoofers that are physically reversed in an array or ground stack.
Product integration by loudspeaker
To implement Product Integration:
Select the Overview tab.
Click the Product Integration button for any output to open the dialog.
Select the loudspeaker model connected to the output from the Product drop-down menu.
Select the lowest DI standard that is common to all models used in the system.
Select the starting point processing to use for this output. The available target phase curve selections are:
pc55-70
pc100
pc125
Systems comprising multiple loudspeaker types with different native phase responses can result in undesired summation or cancellation in the low-mid frequencies. As Meyer Sound improves the native phase response of its loudspeakers, the product integration feature quickly matches the phase responses of mixed loudspeaker models used in a given system.
Product integration is available on every GALAXY processor output.
The native phase curves exhibited by Meyer Sound products can be differentiated by the lowest frequency at which each product deviates by 180 degrees of relative phase. Product integration uses the concept of phase curve families shared by different products: For example, LYON (see the figure below, red line) and LEOPARD loudspeakers both have a low-mid phase response of 180 degrees at 55 Hz (pc55-70); LEO-M (see the figure below, blue line) and UPQ loudspeaker both have a low-mid phase response of 180 degrees at 100 Hz (pc100).
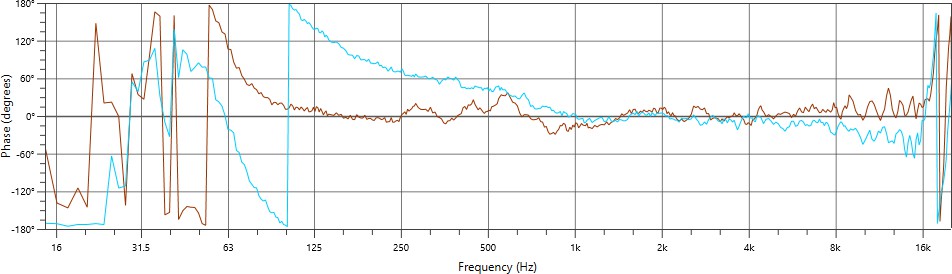
LYON (red) and LEO-M (blue) phase response plots
Product integration example
Product Integration is especially appropriate when applied to loudspeakers that are not in the same native phase curve family. For example, to accomplish product integration for LEOPARD with UPQ-1P:
Enable product integration on both the LEOPARD and UPQ-1P outputs.
Select pc100 for both outputs.
Use pure delay to time align the two loudspeakers at a coverage location where they are equal in level.
Select the Overview tab to verify all loudspeaker system outputs are set to the same phase curve value.
Technical notes
For best results, apply the lowest common phase curve value to different loudspeaker models. For example on the UltraSeries models, pc100 is the lowest common value.
Although the M Series phase response is 180 degrees at 350 Hz, it can be improved by using pc125 when used in close proximity to other Meyer Sound loudspeakers.
When Product Integration is applied to subwoofer outputs, the phase slope is optimized to align with the mid-high loudspeakers using the same phase curve setting.
The changes in phase response caused by product integration are not displayed in Compass, but they can be modeled in MAPP or measured using the transfer function in SIM.
If a delay integration standard is selected that natively exhibits the same phase curve frequency, the output processing will not be altered. For example: LEO-M is natively pc100. If product integration is enabled for LEO-M and set to pc100, no measurable change occurs.